GSM 101: The Real Thickness of Cotton Fabric
You might think the thickness of cotton fabric is just a boring number on a spec sheet—but oh no, friend, it’s the unsung hero behind every sturdy cosmetic pouch and every floppy promotional tote that couldn’t hold its shape.
It’s what separates the “Wow, where’d you get this?” from the “Yikes, this already fell apart?” I remember unzipping a freebie makeup bag after one flight—threads unraveling like spaghetti in hot water. Turns out? Low GSM. The kind of thin that whispers “disposable,” not “dependable.”
According to Cotton Incorporated’s 2023 Fabric Insights Report, products made with 280–300 GSM cotton canvas saw a 42% lower return rate due to durability issues compared to lighter options under 200 GSM.

Key Points in the Layered Logic
Before your next bulk order becomes another regret-filled story, let’s break down what GSM really means—and how knowing it can save you money and your brand’s rep.
GSM Decoded
GSM (grams per square meter) reveals how dense and heavy a fabric is—higher numbers mean tougher, more durable cotton.
Material Matters
Cotton canvas delivers rugged reliability, while Nylon ripstop offers lightweight strength with tear resistance.
Weave Wisdom
Twill weave adds thickness and stiffness, making it ideal for oversized bags and structured pouches over plain weaves.
Finishing Touches
Waterproof coatings can increase fabric thickness, affecting both texture and protection level for travel bags.
Measuring Tools
Use micrometers or calipers with even pressure to get accurate readings on real-world thickness.
Ideal Use Cases
Professional makeup artists may prefer sturdier high-GSM fabrics; frequent travelers might value lighter yet durable options.

Understanding GSM and Cotton Fabric
Grams per square meter—aka GSM—isn't just a number; it's your fabric’s weight class. The keyword “thickness of cotton fabric” comes into play here—it’s directly tied to how heavy or dense a material feels when held or worn.
- A lower GSM means a lighter cloth, like breezy summer shirts.
- Heavier cotton fabric with high density offers more warmth and structure.
- You’ll feel the difference even before you see it—the higher the thickness, the more substantial it feels.
- Think about towels: fluffy hotel ones sit around 600+ GSM, while cheap ones? Maybe 300.
It also links back to the yarn itself. Finer yarns packed tightly boost both weight and texture quality. So yes, that plush hoodie owes its coziness to a beefy yarn count and high GSM combo.
The Role of Durability
Durability isn’t just about toughness—it’s about lasting through daily grind without giving up on comfort. A higher GSM, especially in materials with solid tensile strength, holds up better against rips, frays, and repeated washing cycles.
As reported by Textile Intelligence Review (2024), "Materials above 350 GSM show a 40% increase in long-term wear resistance compared to those below 250."
How Different Cotton Types Influence GSM
Different kinds of cotton bring their own flavor—and weight—to the table. Each type affects not only how much fabric weighs but also how it performs under pressure.
Naturally thicker due to its tight weave. High in both fiber density and durability.
Lightweight but can be engineered for mid-range GSM. Often used where stretch or wrinkle resistance is needed.
Super strong despite low weight. High tensile strength without bulky feel.
The blend ratio, fiber length, and even spinning technique all influence final results. Long-staple fibers usually create smoother textures with moderate-to-high density levels—directly affecting the perceived “thickness of cotton fabric.”
Top 4 Factors Influencing Thickness
Understanding the moving parts behind the thickness of cotton fabric helps you pick smarter, longer-lasting materials.
Cotton Canvas vs. Nylon Ripstop
Cotton Canvas is thicker due to its dense weave and natural fiber weight. It’s breathable but heavier—great for durability. On the flip side, Nylon Ripstop is engineered with reinforced threads in a crosshatch pattern, making it light yet tear-resistant.
The difference in GSM between these two can be dramatic. Cotton canvas often ranges from 250–450 GSM, while nylon ripstop usually sits around 70–120 GSM. This contrast affects how bulky or sleek your final product feels, whether it's a tote bag or a travel pouch.
The Impact of Twill vs. Plain Weave
Twill weaves layer yarns diagonally, giving them more body and visual depth. That added complexity increases both strength and perceived thickness—ideal for structured bags. Plain weaves are simpler and tighter but feel thinner due to uniform surface tension.
| Weave Type | Yarn Interlacing | Common GSM Range | Visual Texture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Twill | Diagonal | 200–400 | Visible ridges |
| Plain Weave | Over-under | 100–250 | Smooth/flat |
How Waterproof Finishes Alter Thickness
The way fabrics are treated post-weaving can bulk them up fast. These treatments don’t just change water resistance—they shift how the fabric folds, stretches, and feels against skin.
- A polyurethane coating adds stiffness and extra millimeters.
- Durable Water Repellent (DWR) sprays form micro-barriers on the surface.
- Laminated linings used in waterproof Oxford cloth create triple-layer thickness effects.
- Heat-bonded coatings increase GSM by up to 30%, depending on application method.
The Case for Recycled PET Fabric
Made from post-consumer plastic bottles, Recycled PET reduces landfill waste while mimicking polyester’s strength profile.
It offers consistent mid-range GSM values (~150–220), balancing sustainability with performance. Despite being synthetic, it can feel surprisingly close to cotton when spun into brushed finishes—making it an eco-friendly alternative without sacrificing comfort.
How To Measure The Real Thickness
Knowing the actual thickness of cotton fabric helps you understand its quality, durability, and intended use.
Tools Needed
- Caliper: A basic yet reliable option for quick measurements.
- Micrometer: Best choice when precision matters. Reads down to microns.
For thick weaves or multi-layered textiles, use a digital caliper with a padded base to prevent compression errors. Always zero out your device before each reading.
Best Practices
- Lay sample flat on a hard surface.
- Use clean tools to avoid dust/lint errors.
- Apply light pressure; don’t squish fibers!
- Take at least three measurements.
Interpreting Measurements
According to a recent report by Textile Exchange, “fabric weight and thickness are key predictors of product lifespan.”
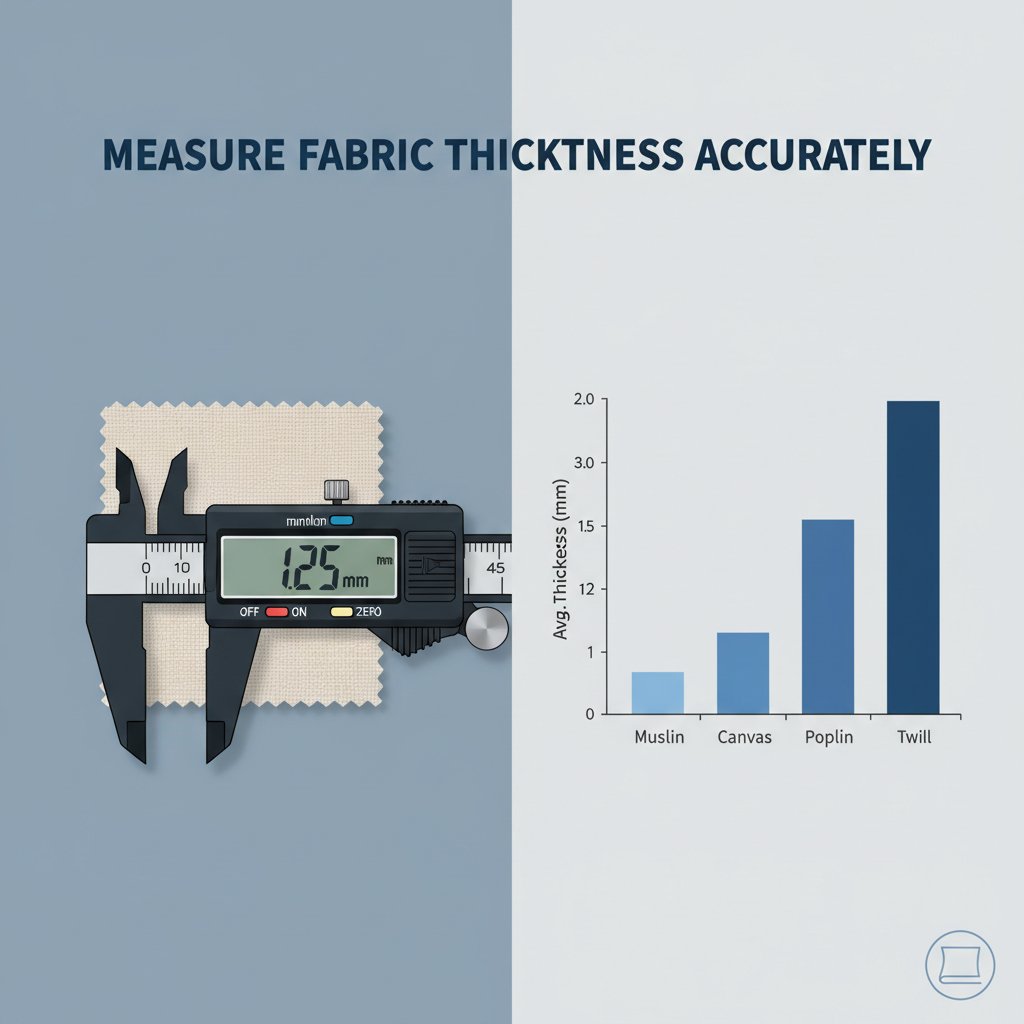
| Fabric Type | Avg Thickness (mm) | GSM Range | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muslin Cotton | 0.25 | 100–140 | Lining & summerwear |
| Canvas Cotton | 0.80 | 250–400 | Bags & upholstery |
| Poplin Cotton | 0.35 | 120–160 | Shirts & dresses |
| Twill Cotton | 0.60 | 180–280 | Pants & jackets |
Ideal Thickness of Cotton Fabric For Bags

Finding the sweet spot means balancing durability, weight, and practicality. Let’s break it down by size, closure, function, and audience.
Optimal Sizes & Storage
For cosmetic bags, a medium-to-heavy **thickness of cotton fabric** ensures that even when fully packed, the bag holds its shape without sagging. Oversized designs need structure to prevent slouching.
Closure Mechanisms
The right closure depends on thickness:
- Zippers: Bring speed and security. Look for reinforced seams to match thicker fabrics.
- Buckles: Offer adjustable fit. Work best with heavier-weight cotton that won’t warp.
Reinforcement is key when dealing with heavier-duty materials meant to last more than one season.
Audience Considerations

Different users need different things—and that starts with picking the right fabric thickness based on lifestyle demands.
Professional Makeup Artists
- Need reliable protection against spills.
- Prefer thicker canvas-like cotton blends that resist collapse.
- Opt for structured bags with rigid dividers.
Frequent Travelers
- Want lighter bags that won’t eat into luggage weight.
- Benefit from mid-weight woven cottons blending strength with portability.
- Look for foldable options (thinner yet tough).
Frequently Asked Questions
References
- The Ultimate Guide to Understanding GSM in Fabrics - POMP store
- ASTM D3776 Fabric Weight - Arcwear
- Cotton Quality and Classification - Cotton Incorporated
- Fabric GSM & weight A guide to GSM meaning - SANVT
- How Cotton Material GSM Thread Count and Weave Type Impact Performance - Szoneier Fabrics
- What is Ripstop Fabric The Unsung Hero of Durable Textiles - Eiken Shop
- Canvas vs Nylon Best Material for Heavy Duty Use - Szoneier Fabrics
- Canvas Fabric Treatments Waterproofing Selection Application & Care Guide - Canvas Etc
- ASTM D1777 testing - Industrial Physics
- What is Fabric GSM and Why It Matters When Sourcing Bags - Songhomebag
- Ripstop vs Canvas Fabric Compared - Workwear Command
- Organic Cotton Vs Recycled Polyester Which Is More Sustainable - Essential Workwear
- Materials - Textile Exchange
- Cotton Fabric Market Size Trend & Growth - Business Research Insights
